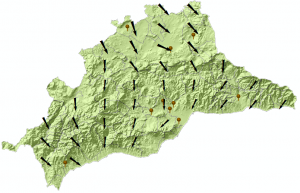
Here we can see the wind map of Malaga (Spain), based on the speed and direction data registered last week in a group of meteorological stations.
To be able to create this map we will follow the next steps.
In the first place we have to generate a layer with the meteorological stations, originated from an Excel table with the UTM coordinates, flux direction (degrees) and speed (m/s) information.
With the command “Add XY data”, we generate a layer of temporary points. After exporting it to a shapefile layer, we will be able to do its geoprocessing.
Using interpolation techniques we obtain a Raster, that estimates the speed and direction wind values for those areas that don´t have meteorological stations. The selected interpolation method is decisive and it will depend on the nature of the variables and the quantity of sampling points. As we don´t have many points, we will use the IDW method.
Following this method we interpolate the values of speed and direction to generate an interpolated raster for each of them. We configure Malaga´s map limit as an extension. Like this we estimate the value of the speed variable.
Through a grid of regular points we can use both Raster values (speed of wind and direction), so that we can represent the magnitude (speed) and direction with vectors .
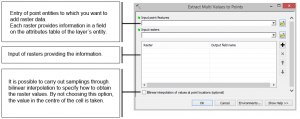
The grid of regular points is generated by selecting “Create fishnet”, and we use the option “Extract Multi Values to Points” to transfer the Raster values of speed and direction to this grid. This way we preserve in its attribute table the values of direction in one field and speed in another, that correspond to the value of the cell on which each point matches.
Finally, we represent the entities by graduated symbology, choosing the speed variable which´s magnitude is represented by the size of the symbol (arrow) and assigning a rotation to the symbol (arrow) to represent the wind direction variable.
Quality training taught by professionals
RECOMMENDED COURSE






Leave A Comment