We have always heard about Open source inside the GIS sector, but when did they appear? what are they useful for? what is their future?

ESRI is the well-known company responsible for developing GIS software, with more than a 30% market share (Câmara, et al., 2012). ArcGIS as well as its other products are a reference in this sector. Even though it offers lots of possibilities and that they are now offering many free resources that can be modified and improved by developers, you still have to buy its programs.

Open source software refers to a tool that is of free access and can have its code source modified. This phenomenon appeared more than 50 years ago which´s term was introduced already in 1998 (Mitasova and Neteler, 2004). Nowadays, Open source GIS tools are experiencing an important expansion and many developers around the world are collaborating to develop new programs that can compete with commercial software so that these technologies can be available and offer alternatives to a bigger number of users.
The Geographic Information Systems [1] world has been revolutionized by these open source and free systems both for their use and development. It is expected that during this year the open source tool Quatum GIS (QGIS) [2] , will be the most used program by users due to is friendly interface, high variety of plugins to carry out diverse operations and its permanent evolution thanks to the synergy between many developers.
These types of programs offer the opportunity to bring closer GIS to users, therefore improving employment rates, and at a low cost.
Other popular open source GIS programs can be found in the following table:
|
Open Source GIS Desktop |
Web |
|
GRASS |
|
|
QGIS |
|
|
uDIG |
|
|
SpatialLite |
|
|
ILWIS |
|
|
SAGA GIS |
|
|
OpenJUMP |
|
|
MapWindow |
|
|
Fmaps |
|
|
gvSIG |
|
|
OrbisGIS |
|
|
OSSIM |
|
|
SEXTANTE |
|
|
KOSMO |
|
|
Thuban |
|
|
GeoDA |
|
|
OpenMap |
|
|
OpenEV |
|
|
Whitebox GAT |
GvSIG
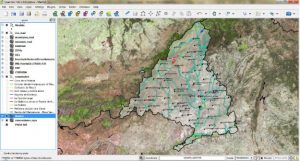
QGIS
We have introduced open source GIS tools, but there has also been advanced progress regarding other software functions such as the display of cartographic information in the web, the creation of metadata or the geoportal design of an organization to create a Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI). We will continue talking about all these in future posts.
Sources:
Câmara, G., Vinhas, L., & de Souza, R. C. M. 2012. Free and open source GIS: will there ever be a geo-Linux?. In Geospatial Free and Open Source Software in the 21st Century (pp. 229-245). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Mitasova H, Neteler M. 2004. GRASS as open source free software GIS: accomplishments and perspectives. Transactions in GIS, 8(2):145-154.
Wiki OSGeo: http://wiki.osgeo.org/wiki/Rese%C3%B1as_FOSS4G
Free GIS: http://www.freegis.org/
Wikipedia, List of geographic information systems software: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_geographic_information_systems_software#Desktop_GIS
GIS Corps: http://www.giscorps.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=13&Itemid=48#Desktops
Quality training taught by professionals
RECOMMENDED COURSE




Leave A Comment